GeoJSON is a geospatial data format that has become quite popular in the last few years. This blog post discusses what GeoJSON is, how you can create it and some Esri tools that enable using the format.
What is GeoJSON?
The GeoJSON data format is a data format based on the open data standard JSON, which is short for JavaScript Object Notation. JSON is the most common data format used for asynchronous browser/server communication and uses text to transmit data objects consisting of attribute–value pairs. The format is easy to read and offers web developers an easy way to extend existing APIs.
The GeoJSON format was designed for the representation of simple geographical features, along with their non-spatial attributes and now supports a number of geometry types such as points, line strings, polygons and multi-part collections of these types. GeoJSON was created and maintained by an internet working group of developers. Since the first GeoJSON format specification in 2008, the adoption of GeoJSON in spatial databases, web APIs, and open data platforms has grown significantly, resulting in a need for standardization. This led to the creation of a Geographic JSON working group which released a RFC document on GeoJSON in August 2016. GeoJSON uses either .json or .geojson as filename extension.
Create your own GeoJSON
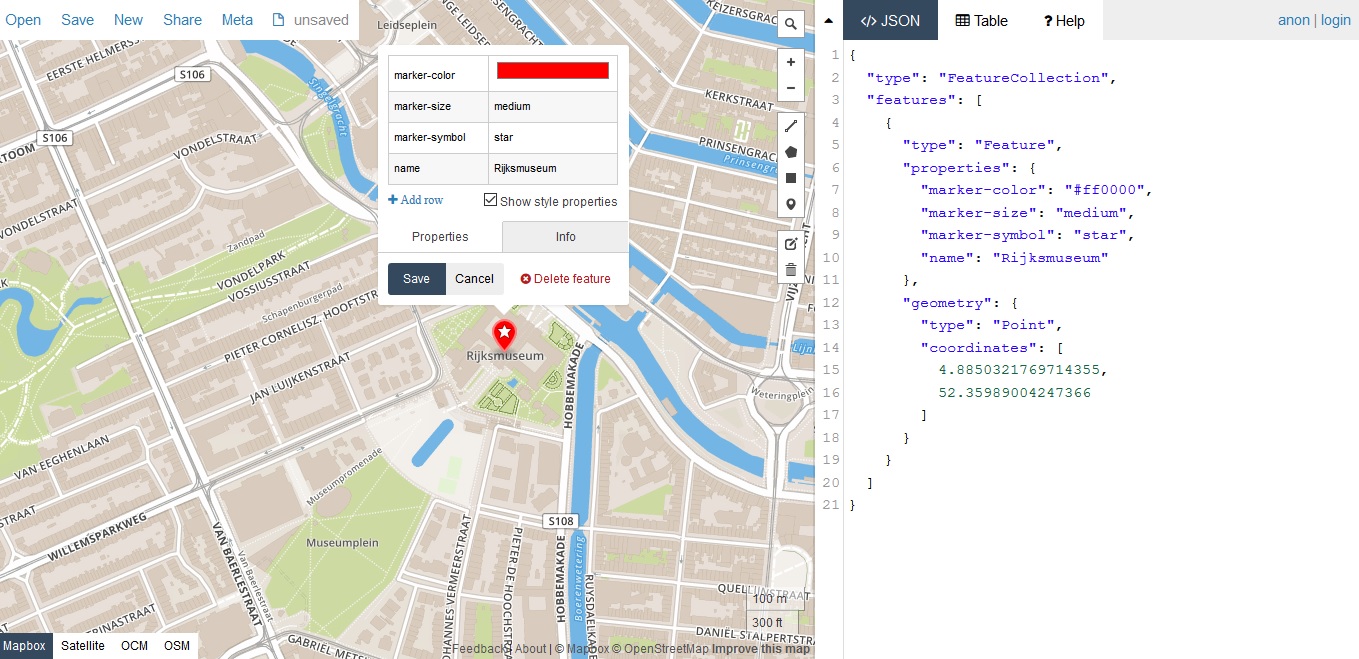
A great resource for creating your own GeoJSON data is http://geojson.io, which enables you to draw features on a map, and optionally, add non-spatial attributes to these features in a code editor and save the results in a variety of data formats, such as GeoJSON.
GeoJSON is supported differently by numerous mapping APIs, GIS software packages and companies such as Mapbox, Carto and Safe Software. The following covers Esri support for the format.
Esri support for GeoJSON
Since December 2014, Esri supports publishing and downloading as GeoJSON in ArcGIS Online. Also, all hosted feature services as can be accessed as GeoJSON by adding the f=geojson query parameter. Esri also created an open-source JavaScript library called Terraformer, which is a geographic toolkit for dealing with geometry, geography, formats, and building geo databases. It consists of a collection of modules, such as the Terraformer core module that contains methods and objects for working with GeoJSON. Terraformer is designed to work in NodeJS and in a web browser. Esri also created Koop, a JavaScript toolkit for connecting incompatible spatial APIs. Out of the box it exposes a Node.js server that can translate GeoJSON into the Geoservices specification supported by the ArcGIS product family.
ArcMap and ArcGIS Pro do not offer native support for GeoJSON, but the Data Interoperability extension offers read and write support for the format. The system toolbox “Conversion” in ArcMap offers “a Feature to JSON” and “JSON to Features” tool (in Pro, refer to “JSON toolset). The same can be attained with the “AsShape” function in ArcPy. There’s also a Python package called “geojson” for encoding and decoding GeoJSON formatted data and offers classes for all GeoJSON Objects.