Read Part 1
Read Part 2
Read Part 3
Read Part 4
Read Part 5
Part 6: Geodatabase Development and Automation
Welcome to the sixth installment of our ArcGIS Geodatabase series. In this article, we’ll explore the powerful world of geodatabase automation, focusing on Python scripting with ArcPy, custom geoprocessing tools, and database administration techniques that will streamline your GIS workflows and enhance productivity.
Introduction to Geodatabase Automation
Geodatabase automation transforms repetitive, time-consuming tasks into efficient, repeatable processes. Whether you’re managing hundreds of feature classes, performing regular data updates, or maintaining complex spatial relationships, automation ensures consistency while freeing up valuable time for analysis and decision-making.
The benefits of automation extend beyond efficiency. Automated processes reduce human error, provide consistent documentation, enable batch operations, and create scalable solutions that grow with your organization’s needs.
Python and ArcPy: The Foundation of Geodatabase Automation
ArcPy serves as the cornerstone of ArcGIS automation, providing comprehensive access to geoprocessing tools, data management functions, and geodatabase operations through Python scripting.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
Before diving into automation scripts, establish a proper development environment. Install Python with ArcGIS Pro or ArcGIS Desktop, configure your IDE with ArcPy libraries, and create a structured project folder for your scripts.

Essential ArcPy Functions for Geodatabase Management
Understanding core ArcPy functions forms the foundation of effective automation. The arcpy.ListFeatureClasses() function inventories your geodatabase contents, while arcpy.Describe() retrieves detailed information about spatial datasets.
Data management operations like arcpy.management.CreateFeatureclass() and arcpy.management.AddField() enable programmatic geodatabase construction. Cursor objects provide row-level access for data manipulation, with arcpy.da.SearchCursor() for reading, arcpy.da.InsertCursor() for adding records, and arcpy.da.UpdateCursor() for modifications.
Automating Common Geodatabase Tasks
Consider a scenario where you need to standardize field names across multiple feature classes. Manual updates would be tedious and error-prone, but automation makes this task straightforward.

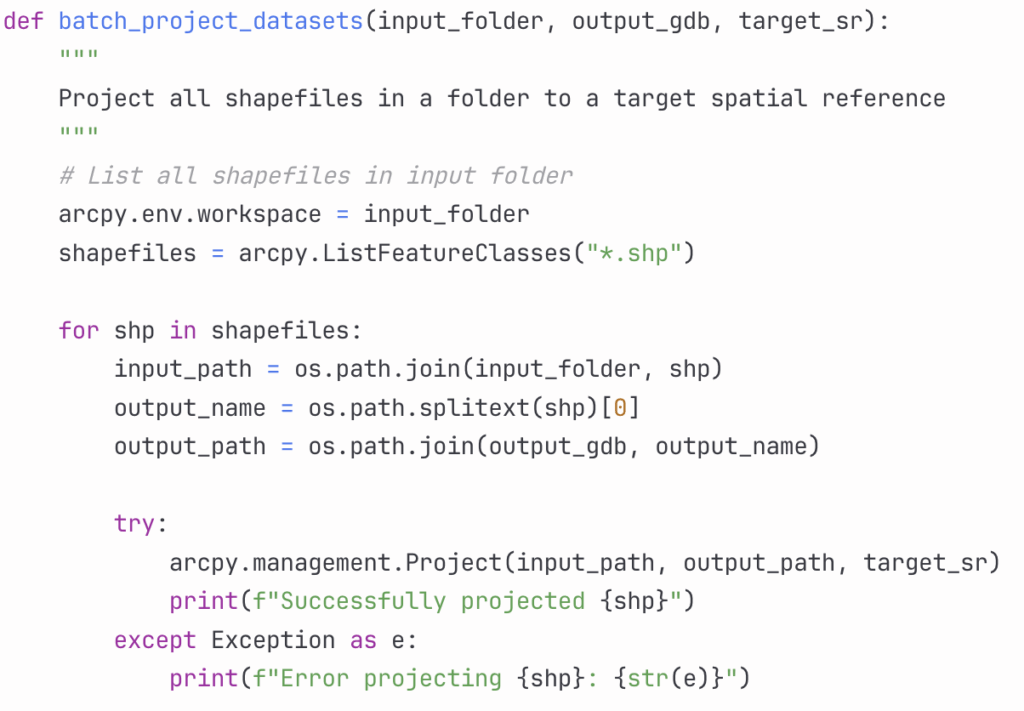
Creating Custom Geoprocessing Tools
Custom geoprocessing tools extend ArcGIS functionality by packaging your Python scripts into user-friendly tools that integrate seamlessly with the ArcGIS interface.
Script Tool Development Process
Creating a script tool involves several key steps: developing and testing your Python script, defining tool parameters, creating the toolbox structure, and configuring the tool interface.
Start by developing a robust Python script that handles parameters, includes error checking, and provides user feedback. Your script should accept parameters through arcpy.GetParameterAsText() and communicate progress using arcpy.AddMessage().

Tool Parameter Configuration
Effective parameter configuration ensures your custom tools are intuitive and robust. Define parameter data types, set default values, establish parameter dependencies, and implement validation rules.
Consider creating parameter groups for complex tools, use appropriate input filters, and provide clear parameter descriptions. Dynamic parameter lists can adapt based on user selections, while parameter validation prevents common errors.
Advanced Tool Features
Sophisticated custom tools incorporate progress reporting, detailed logging, and comprehensive error handling. Implement transaction support for database operations, create tool documentation, and consider multi-threading for performance-intensive operations.

Database Administration Scripting
Database administration scripting automates routine maintenance tasks, monitors geodatabase health, and ensures optimal performance through systematic management procedures.
Geodatabase Maintenance Scripts
Regular maintenance prevents performance degradation and ensures data integrity. Create scripts that analyze and rebuild spatial indexes, update statistics for query optimization, and compress geodatabases to reclaim space.

Monitoring and Reporting Scripts
Effective database administration requires continuous monitoring. Develop scripts that track geodatabase size, monitor performance metrics, identify potential issues, and generate regular reports.

Backup and Recovery Automation
Automated backup strategies protect against data loss and enable quick recovery. Implement scheduled backups, version control for geodatabase schemas, and automated testing of backup integrity.

Best Practices and Performance Optimization
Successful geodatabase automation requires adherence to established best practices and continuous performance optimization.
Code Organization and Documentation
Structure your automation scripts with clear organization, comprehensive documentation, and consistent coding standards. Use meaningful variable names, implement proper error handling, and create reusable functions that can be shared across projects.
Maintain version control for your scripts, document parameter requirements, and provide usage examples. Consider creating a standard template for automation scripts that includes logging, error handling, and parameter validation.
Performance Considerations
Optimize your automation scripts by minimizing geodatabase connections, using appropriate cursor types, and implementing efficient query strategies. Batch operations when possible, avoid unnecessary spatial operations, and monitor memory usage for large datasets.
Consider parallel processing for independent operations, implement progress tracking for long-running scripts, and use appropriate arcpy environment settings to optimize performance.
Error Handling and Logging
Robust error handling ensures your automation scripts can gracefully handle unexpected situations. Implement try-catch blocks, validate inputs before processing, and provide meaningful error messages.
Comprehensive logging enables troubleshooting and performance monitoring. Log script execution times, record processing statistics, and maintain audit trails for critical operations.
Integration with Enterprise Systems
Modern geodatabase automation often requires integration with enterprise systems, web services, and external databases. Develop scripts that can consume REST services, interact with enterprise databases, and integrate with workflow management systems.
Consider authentication requirements, implement secure credential management, and design scripts that can operate in enterprise environments with appropriate security measures.
Conclusion
Geodatabase development and automation represent essential skills for modern GIS professionals. Through Python and ArcPy scripting, custom geoprocessing tools, and systematic database administration, you can transform manual processes into efficient, reliable automated workflows.
The techniques covered in this article provide a foundation for building sophisticated automation solutions that scale with your organization’s needs. As you implement these approaches, remember that successful automation requires careful planning, thorough testing, and ongoing maintenance.
In our next article, we’ll explore advanced geodatabase topics including enterprise deployment strategies, cloud integration, and emerging technologies that are shaping the future of spatial data management.
Continue building your geodatabase expertise, and don’t hesitate to experiment with these automation techniques in your own projects. The investment in learning these skills will pay dividends in increased productivity and more reliable GIS operations.

